Introduction
Think about getting on a bus or train with no driver, but it still takes you to your stop safely and on time. That’s what autonomous public transport means. It’s not just an idea anymore. Around the world, cities are beginning to test and adopt this kind of travel.
In this blog, we’ll talk about how this works, why it’s useful, what problems it might face, and how countries like India are preparing for it. We’ll also look at how people, businesses, and governments can benefit from starting early. Whether you’re into smart tech, cleaner cities, or better travel, there’s something here.

What Is Autonomous Public Transport?
This term means public transport that runs without a driver like buses, metros, or shuttles that move on their own using smart technology. These vehicles use:
- AI Technology
- Cameras and sensors
- LIDAR and radar
- GPS for accurate location
- Maps and real-time updates
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication
These tools help the vehicle understand what’s around it and make smart choices, just like a human would, but often with more accuracy.
This isn’t just about removing drivers. The goal is to make the journey more comfortable & safe. As the tech gets better, these vehicles are also getting smarter at dealing with real traffic on the roads.
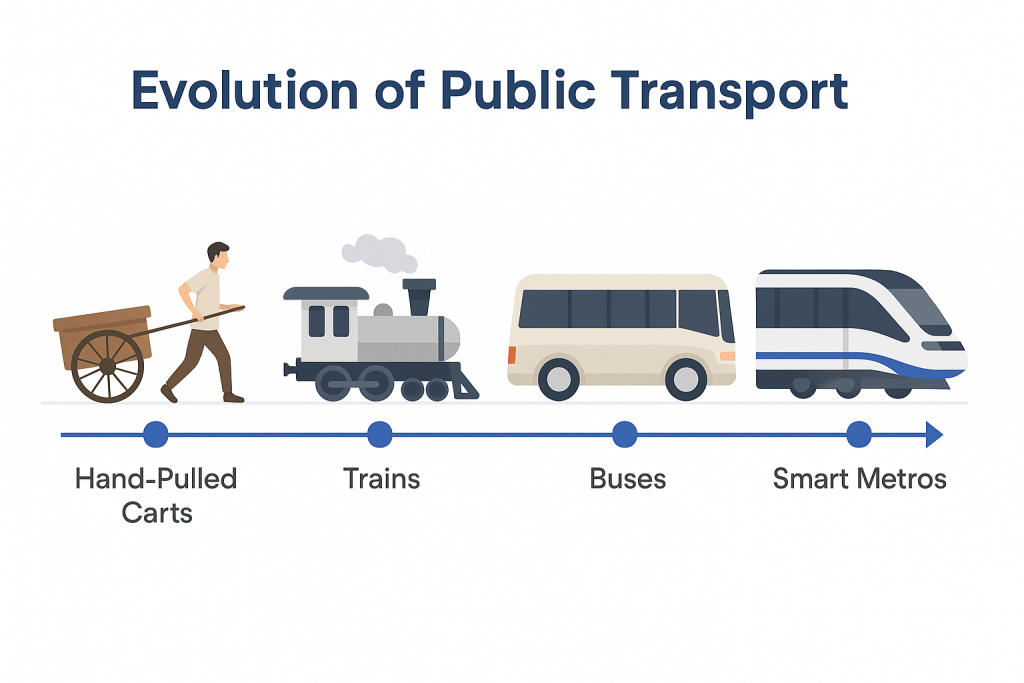
How Public Transport Has Changed Over Time
Public transport has changed a lot with time. We’ve gone from developing carts and old trains to metro trains. It is used to give safety and comfort.
Now, we’re implementing a new way of transport. It’s not just about speed or size anymore it’s about using things like AI tech, and green energy to make journeys safer by reducing traffic and pollution.
Tech That Makes It Possible
1. AI and Learning
AI is what helps these vehicles “think.” They learn from past experiences to get better with time.
2. Cameras and Sensors
These act like the eyes of the vehicle. They see the road & passage, traffic, signs, and even people nearby.
3. LIDAR and Radar
They measure distance and speed, even in rain or at night.
4. GPS and Maps
Helps the vehicle know where it is and follow the best route.
5. V2X
This lets vehicles talk to each other and things like traffic lights. It helps reduce delays and makes roads safer.
Why Autonomous Transport Is Useful
- Fewer Accidents: Most road accidents are caused by people making mistakes. A machine that follows rules and never gets tired or distracted can lower these risks.
- Saves Money Over Time: Once up and running, these vehicles don’t need a driver’s salary. Electric ones also need less maintenance.
- Helps Everyone Get Around: People who can’t drive like elderly people or those with disabilities can use these services easily.
- Better Traffic Flow: When vehicles share data and work together, traffic becomes more organized and smooth.
- Better for the Environment: Most automatic vehicles are electric, so they don’t produce smoke and keep pollution in control.
- To explore more about how India is investing in future mobility, check out our post on Investing in Electric Vehicles and Green Hydrogen.
Countries Where it is already adapted
Singapore
Testing driverless buses in specific areas. More services are planned.
Finland
Running small driverless buses in urban zones. Public reaction has been positive.
America
In some cities, people have started using a taxi that works without drivers from companies like Waymo and Cruise. It’s not just a test anymore—it’s part of daily life for some. It’s not the upcoming future cause—it’s happening.
Germany and France
Trying out driverless trains and buses in selected zones.
China
Cities like Shenzhen and Beijing are trying to start driverless taxis. Their local companies are developing and using different models from other companies.
How India Is Getting Ready
India hasn’t launched full-scale autonomous public transport yet, but things are moving in that direction.
Ongoing Projects
- Delhi Metro has started using automation on some lines.
- Kochi Water Metro uses GPS to help with navigation.
- Some tech parks in Bengaluru and Hyderabad are testing autonomous shuttles.
Government Support
- Smart Cities Mission promotes smart transport.
- Electric Mobility Mission supports clean vehicles.
- Atal Innovation Mission backs startups in tech and AI.
- According to a NITI Aayog strategy report, India aims to become a global leader in electric and autonomous mobility by investing in smart infrastructure and innovative technologies.
What’s Holding It Back
- Roads Not Ready: Many roads don’t have clear lanes, signs, or smooth surfaces.
- Rules Are Missing: There are no official rules about how to run or insure these vehicles.
- People Are Unsure: Many people still feel nervous about getting into a vehicle with no driver.
- It’s Expensive: Buying the tech, setting up the system, and running tests all cost a lot.

Startups and Big Companies in India
Several Indian startups are working on this:
- Minus Zero: Uses only cameras to help vehicles drive on their own.
- Swaayatt Robots: Focuses on Indian traffic conditions..
- HiTech Robotic Systemz: Builds smart systems for logistics and transport.
Big companies like Tata and Mahindra are also spending money on research to prepare for automation.
Skills and Jobs
As driverless transport grows, new types of jobs will be needed:
- AI Programmers
- Fleet managers
- safety and maintenance staff
- Urban Designers for Smart transport
- Traffic and data analysts
Designing Smarter Cities
For these vehicles to work well, cities need to be updated. That includes:
- Lanes only for AVs
- Smart traffic lights
- Charging stations
- Control rooms to monitor everything in Real-time.
Urban planners will have to think differently when designing future roads and neighborhoods.
Learning from Other Countries
- USA: Some states allow AV testing freely.
- UK: Wants full rollout by 2025.
- Japan: Used AVs during the Tokyo Olympics.
India can adapt these ideas to build its own rules.
What Might Happen by 2030
By 2030, we might see:
- Autonomous shuttles in offices and airports.
- Metro lines with no drivers.
- Dedicated roads for AVs.
- Mobile apps for booking rides with real-time updates.

It will take time, but change is already happening.
Final Words
Autonomous transport isn’t just a fancy idea anymore. Many countries have already started using driverless public transport, showing real benefits—like making travel safer, cutting costs, and giving more people access to reliable transport.
India does have its challenges, but with its skilled people, growing tech scene, and strong government support, it has what it takes to make this a reality. With smart planning, clear rules, and public support, driverless transport could become part of everyday life here too.