Introduction
Tariff Changes India 2025 are creating a major buzz this year. If you’ve been wondering what all the buzz is about with India’s 2025 Budget, you’re not alone. This year’s budget has brought some major changes, especially in how taxes and tariffs are handled. These updates are a big deal—they’re set to change the way India does business, both at home and abroad. So what exactly has changed? And more importantly, how does it affect businesses and regular people like us?
For more details, you can refer to India’s 2025 Budget official announcements outlining the complete economic reforms.
Stay tuned — I’ll try to explain it to you in the simplest way possible.
Why Tariffs Are Critical for Economic Growth
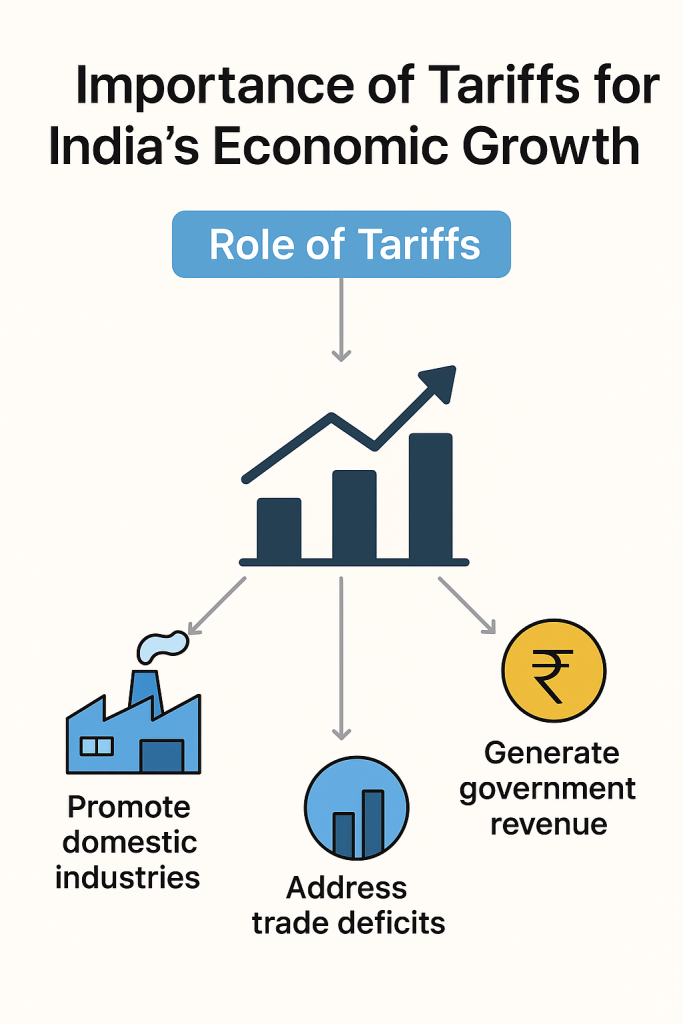
Tariffs influence the price of goods, industrial growth, global trade relations, and even the daily cost of living. They serve as:
- Tools to protect local industries
- Instruments to regulate trade deficits
- Levers to encourage domestic manufacturing
- Sources of government revenue
- Means to foster strategic self-reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat)
For a developing economy like India, strategic tariff policies can be the difference between being an import-dependent nation and becoming a global manufacturing hub.
A Decade in Review: India’s Tariff Policy Evolution (2015-2025)
But from last ten years, India has been handling tariffs differently:
- 2015-2017: started a campaign for Make in India; Increased tariffs on electronic items, and luxury goods.
- 2018-2020: Tariff support for steel, aluminum, textiles; tightening against Chinese imports.
- 2020-2022: Pandemic-driven exemptions on medical equipment and healthcare imports.
- 2023-2024: Green energy push; concessional rates on EV and renewable components.
- 2025: Massive simplification, strategic realignment with global standards, and support for critical sectors.
Key Announcements: Tariff Reforms in Budget 2025
The Union Budget 2025 brought sweeping changes:
- Basic Customs Duty (BCD) slabs reduced from 21 to 8.
- Strategic exemption of tariffs for life-saving drugs.
- Safeguard duty of 12% on steel imports.
- Duty-free imports for EV battery manufacturing components.
- Protective duties on textiles and display panels.
- Duty reductions on raw materials critical for manufacturing industries.

Sector-Wise Breakdown of Tariff Changes
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Excluded from duties for 30 to 36 life-saving drugs. Concessional duties for another six critical medicines—expected impact: reduced healthcare costs for millions of Indians.
Electronics and Consumer Technology
Reduction of duties on LED/LCD. Increase in finished product duties to 20% to boost domestic assembly. Mobile battery component imports made duty-free to strengthen India’s electronics manufacturing base.
Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy
No duty on 35 EV battery components. Incentives for solar panel manufacturers. Support for Indian EV Companies like Tata Motors and others.
If you’re interested in how electric vehicle opportunities are growing in India after these tariff reforms, don’t miss our guide on how to invest in electric vehicles.
Textiles and Apparel
Boost for domestic garment and textile manufacturers who compete against low-cost imports from Bangladesh and Vietnam.
Metals and Mining
Duties reduced on necessary chemicals like Glycerol, Phosphoric Acid, Boric Acid, and unwrought Tin. Relief for metal processing and chemical industries.
Steel
A temporary safeguard duty of 12% was applied on importing steel to protect the local sector against Chinese dumping.
Leather and Footwear
Duty changes aimed at promoting domestic manufacturing and reducing dependency on imported finished products.
Simplified Customs Duty Structure: A Landmark Reform
Previously, India’s customs structure had 21 different slabs ranging from 5% to 150%. Such a complex structure often led to confusion, disputes, and administrative inefficiency.
By reducing the number of slabs to just 8 (including 0% duty), India:
- Simplifies tax compliance
- Enhances transparency
- Encourages trade and investment
- Decreases disputes between traders and the government
Strategic Countermeasures Against Chinese Imports
One of the subtle but important themes of the 2025 Budget is the strategic shift away from dependency on Chinese imports:
- Safeguard duties on steel.
- Duty increases on imported electronic finished goods.
- use our own battery and solar panel.
The government’s policy indirectly pressures industries to develop local alternatives and aligns with broader geopolitical shifts.
Real-World Examples: What Gets Cheaper or Costlier?
Cheaper:
- Life-saving medicines
- Mobile phones assembled in India
- Electric vehicles and solar panels
Costlier:
- Fully imported smartboards
- Imported premium garments
- Luxury steel furniture made from imported steel
Business and Consumer Impact Explained
Impact on Businesses
Positive impacts:
- Lower raw material costs in critical sectors
- More competitive exports
- Higher margins for domestic manufacturing
Challenges:
- Importers can’t survive without ready-made goods and may need to find new market chains.
- Industries needing professional parts not yet available in India could face short-term issues.
Impact on Consumers
For consumers, the picture is mostly positive:
- Cheaper healthcare and electronics
- Slight price hikes on luxury imports
- Better availability of locally manufactured EVs and green tech products
You know, right now India’s working on some big trade deals with places like the European Union, UK, Australia, and UAE.
To make things easier, they’ve started cutting and simplifying taxes on some products.It’s like making ourselves more “business-friendly,” so more countries want to trade with us.
Plus, it helps India stand stronger against countries like Vietnam and Indonesia which are already big players in exports.
Challenges and Critical Voices
While the reforms are progressive, some concerns remain:
- Increased protectionism in textiles could affect long-term global competitiveness.
- SMEs will face problems to do work with the new supply chain.
- we will still Depend on other countries for semiconductors.
Experts also caution that tariffs should be supported by infrastructure development, ease of doing business reforms, and skilling programs to fully realize the benefits.
Future Outlook: Toward a Trillion-Dollar Manufacturing Economy
The tariff reforms are only the beginning. In the upcoming time, India is going to:
- Expand tariff concessions for digital economy sectors.
- Provide new policies for semiconductor missions.
- Develop specialized economic zones (SEZs) with duty-free regimes.
- Try to increase technologies like green energy, AI, and biotech.

Honestly, if India also gets better with stuff like transport, labor rules, and tech upgrades, we can seriously end up being one of the top places in the world to manufacture things.
It’s not just about taxes — everything working together, you know?
Conclusion
Honestly, the 2025 Budget made some smart moves with these new tariff changes.
They’re not just random updates — they’re pushing India closer to that big $5 trillion economy dream we keep hearing about. By making things simpler, protecting important industries, and giving manufacturing a good boost, India is taking some serious steps forward.
Now it’s not just up to the government — businesses, regular people, everyone’s gotta play their part to make the most out of this.
(FAQs)
Why are tariffs important?
Tariffs are taxes applied on goods imported from other countries. They help protect domestic industries, generate government revenue, promote local manufacturing, and balance trade deficits.
How many basic customs duty slabs exist after the 2025 reforms?
After the 2025 Budget reforms, India has simplified its basic customs duty structure from 21 to 8 slabs, including a zero rate.
Which sectors are the biggest beneficiaries of the new tariff changes?
Key beneficiaries include healthcare, electronics, electric vehicles renewable energy, and textiles.



