Introduction
In 2008, at the height of the world’s worst financial crisis in decades, an unwitnessed protagonist arrived with a new idea that would provide a shock to the global finance system: Bitcoin, or at least the idea of it. It was not just a digital currency; it was more of a repudiation of the traditional banking system’s flaws. Who was Satoshi Nakamoto, and why specifically did he create Bitcoin?

This blog aims to examine the history of Satoshi Nakamoto, the role banks played in the 2008 financial crisis, and the design of Bitcoin as a safer alternative to the traditional, centralized financial system. In addition, we’ll explore how it functions and why it holds the potential to shape the future of global finance.
The Flaws in the Old Banking System
The Origins of Money
Before we can understand Bitcoin, we need to understand how money came about:
- From the beginning: people exchanged goods we now classify as food, cloth, and land.
- Barter system: people traded items directly without using a standard unit of value
- Gold/Silver: kings began using gold and silver as their currency.
- Centralized system: with kings and ministers controlling the majority of the wealth.
The Rise of Merchants and Trade
- Smart individuals began producing consumables and luxury products.
- Merchants traded goods more and more, thus holding the power alongside the king.
- Eventually—and we all know the story—capitalism happened and business became the impetus vendors and manufacturers were exploiting.
The Birth of Modern Banking
- Kings borrowed gold from merchants to fund their wars, trading benefits in return.
- Over time, the merchants learned how to give out loans with interest.
- Banks sprung up, collected money from depositors, and lent money out for their profit.
The Problem with Modern Banks:
Banks started loaning out much larger amounts than the money they had, as was sometimes done for fun:
- Theoretically, if a bank received a deposit in cash of ₹5 lakh, they could loan out ₹15 lakh.
- The founding idea relied on a few assumptions: that patrons would not all withdraw their money at the same time and that borrowers would pay their loans down with interest.
But what if things all go wrong?
2008 Financial Crisis
- US banks extended home loans to people who couldn’t pay them back.
- These risky lending practices were backed by fraudulently rated and indiscriminately invested financial instruments.
- The bubble burst. 10 million people in the United States became homeless – overnight.
This crisis demonstrated the fragility and corruption of modern banking.
The 2008 global financial collapse was a key trigger for the creation of Bitcoin. To understand the full scope of what happened, read this official account by the Federal Reserve on the Global Financial Crisis.
Satoshi Nakamoto & Bitcoin
Who is Satoshi Nakamoto?
- An anonymous person (or group of people) who launched Bitcoin in 2009.
- Owns over 1.1 million Bitcoins, worth billions of dollars, but has never spent even one of them.
- Disappeared after launching Bitcoin, leaving a fully functioning system behind.
Why Did Satoshi Create Bitcoin?
- Had a negative experience with the 2008 crisis and manipulation of money by banks and governments.
- Wanted to create a decentralized currency:
- Limited supply (21 million coins total)
- Zero Rules by any bank or government
- Transparent and peer-to-peer
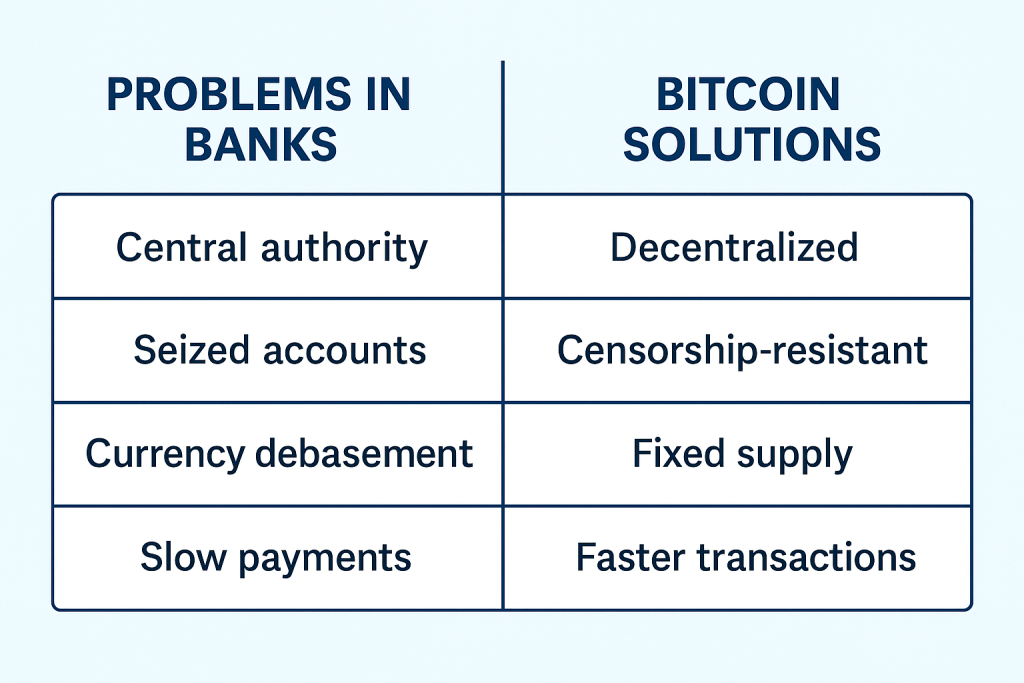
How Bitcoin Might Help with Banking Problems
The problem in Banks Bank’s Solution
Centralized banking control Decentralized network
Unlimited ability to print money 21 million coins limited supply
Risk of zero confidence and financial Predictable and transparent protocol
We have a loan-based economy Spend only what you have.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
- Each transaction is recorded on blockchain technology.
- Miners verify transactions and help secure the network.
- Anyone with an internet connection can send or receive bitcoin and there is no third party involved!
The First Use Cases of Bitcoin
- WikiLeaks accepted Bitcoin payments after being banned by PayPal, Visa, and Mastercard.
- Satoshi was understandably concerned this would get unknown exposure.
The Reason Satoshi Stayed Anonymous
- Being public about his identity could’ve made him a target.
- Bitcoin disrupted an existing model that many countries and companies relied on; the model of utilizing debt.
- He stayed anonymous to protect himself and the whole movement.
Bitcoin as a Disruption:
- Governments can’t shut it down due to its decentralized nature.
- Governments can’t stop transaction flow because there is no central authority.
- A true peer-to-peer currency, with no borders, has emerged.
Bitcoin and its Global Impact on Finance
Real-World Impact of Bitcoin
- Remittances- People send money across borders almost free of fees utilizing Bitcoin.
- Freedom from inflation- Countries that experience currency instability (eg Venezuela, Zimbabwe, etc) have started using Bitcoin when their own country is unstable, as a way to store their wealth, which in these other countries is next to meaningless due to hyperinflation.
- Banked individuals- Individuals who do not have bank accounts can access money in digital form, simply by having a phone with internet.
- Entrepreneurs- More small businesses accept Bitcoin for goods and services, whereas prior they would never have accepted non-fiat payments, eg coffee shops, farms, tech startup.

Global Adoption of Crypto
- El Salvador became the first country to officially accept Bitcoin as a currency in 2021.
- The trend of individuals actively adopting crypto continues to grow, with a lot of countries with significant inflation rates actively being an example.
- Global investment- Thousands upon thousands of crypto startups have launched and have wallets and exchanges globally as a great global rise, including ATMs and payments in stores as astounding as Tesla and Square.
Reasons Governments Are Averse to Progress
- Loss of control: They cannot regulate Bitcoin like fiat currency.
- Threat to monetary policy: Central banks cannot print more Bitcoin to influence the economy like traditional currency.
- Concerns regarding crime: For the sake of Bitcoin, concerns exist about usage in illegal transactions (most fiat currency is also used to facilitate crime).
- Tax and tracking issues: Crypto undermines the traditional method of tracking financial transactions.
How Governments Are Reacting To Bitcoin
Country Legality Attitude toward Bitcoin
El Salvador Legal tender
USA Heavily regulated by tax laws and registered SEC firm
China Outlawed cryptocurrency trading and mining in 2021
India Taxes income derived from crypto but stops short of a ban (cautious)
Bitcoin’s Future
Mass Adoption of Bitcoin:
- It is unlikely that Bitcoin will replace fiat currency completely, as it will likely become common practice to invest in crypto akin to making investments in gold as a form of store of value (AKA the new “digital gold” – a supplement to today’s fiat currency).
Improved Technologies Surrounding Bitcoin
- Lightning Network, a second-layer option is being tested; it will provide speedy and cost-effective transactions (currently).
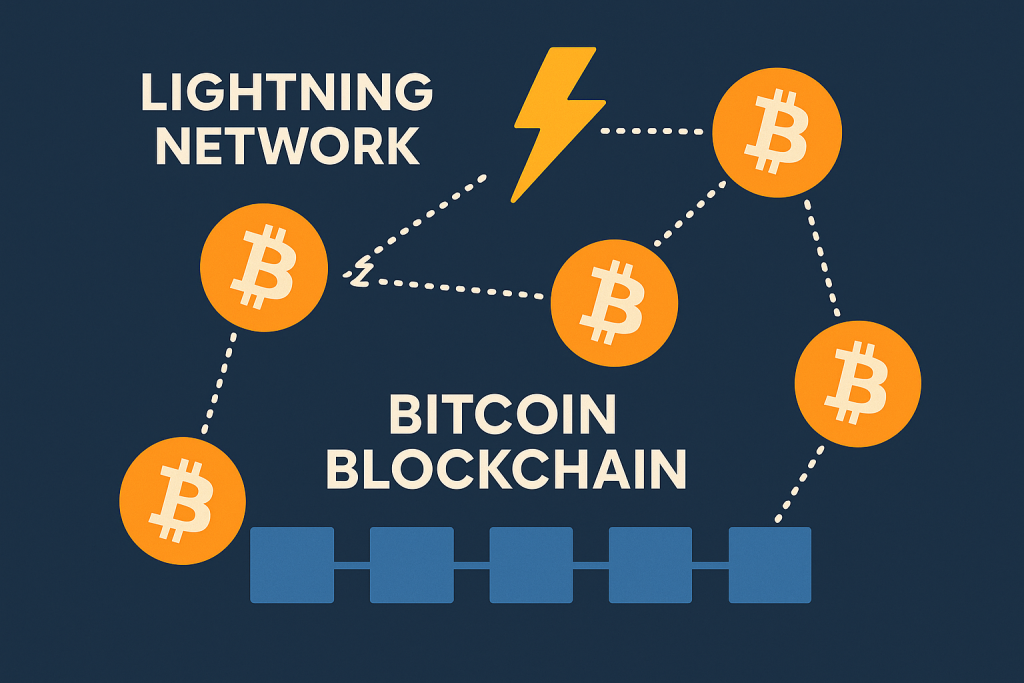
- Additional technology layers are being developed in the Bitcoin ecosystem to improve scalability and support wider adoption.
More Institutional Interest
- More businesses and governments will likely hold Bitcoin as a reserve asset (a form of currency).
- Banks will likely offer crypto services rather than resist.
A Different Financial System
- Borderless, decentralized, and inclusive.
- Bitcoin may be the on-ramp to a form of the future digital economy.
Final Thoughts
- Bitcoin is more than just a currency. It’s a movement. A movement towards transparency, equality, and decentralization. What began as a silent protest against the 2008 financial crisis, has become a global revolution.
- The more people understand Satoshi Nakamoto’s vision, the more they realize they are not just buying a coin, but buying into a better future.
Conclusion
The struggle between Bitcoin and banks is not a battle between technology and tradition but between freedom and control. Satoshi Nakamoto developed Bitcoin with the goal of giving financial power back to the people. Whether Bitcoin is the currency of the future or not, one thing is for certain, it has changed the world as we know it, forever.
If you enjoyed and found value in this article share it publicly. If you want to learn more about how Bitcoin works in-depth, we have a guide on blockchain coming out soon!
As traditional banks face disruption from decentralized systems, you can also explore how to master Web3 without coding and be part of the new financial era.



